What are the distinctions: public cloud vs private cloud vs hybrid cloud?

Just like the clouds in the sky, cloud solutions come in various forms. In cloud computing, there is a clear distinction between public cloud, private cloud, and hybrid cloud. How do you make the right choice for your data? Where do the differences lie? And which cloud services does Combell offer to support you? It's time to take a look at the clouds, the ones where you store your data.
- What you need to know about public clouds
- What you need to know about private clouds
- What you need to know about hybrid clouds
- Which cloud is suitable for your company?
- Importance of cloud services
- 1. What are the terms and conditions?
- 2. Is there support provided?
- 3. How solid is the Service Level Agreement (SLA)?
- 4. Do you get guarantees when something goes wrong?
- 5. What about the "Nines"?
- 6. How reliable is the provider?
- 7. What about the technological requirements of cloud computing?
- 8. Do you have a sufficient budget?
- 9. How secure are your Data?
- Your needs and requirements as our starting point.
What you need to know about public clouds
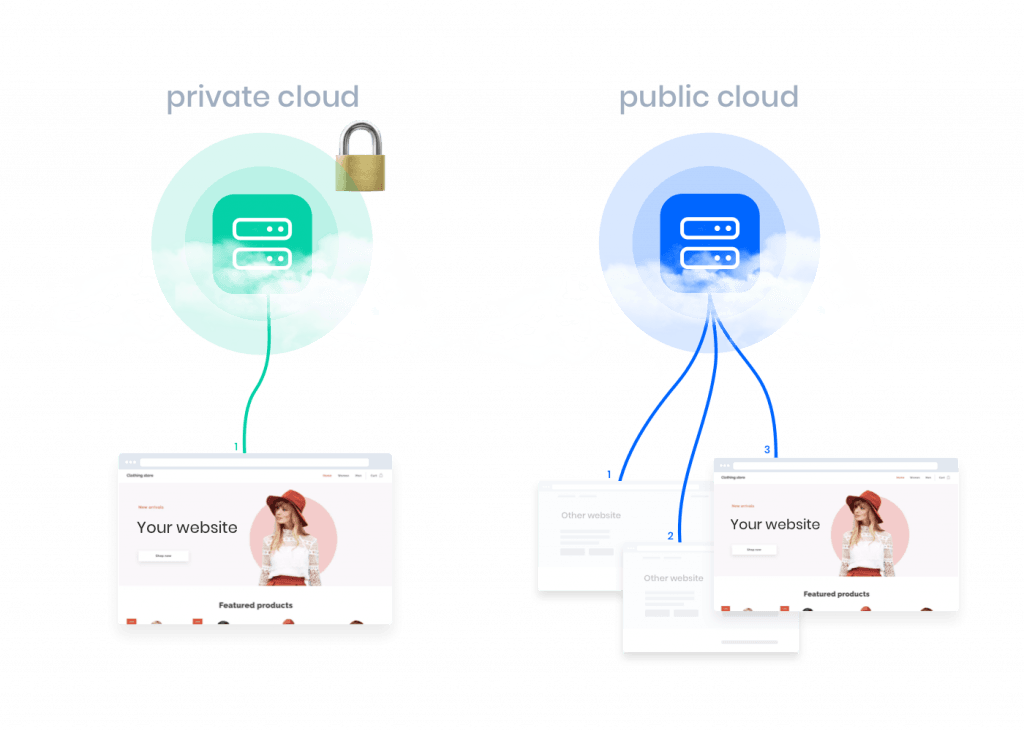
The primary distinction between a public cloud and other cloud solutions (such as private cloud, hybrid cloud, etc.) lies in infrastructure and ownership. In a public cloud, you share your resources with other customers and no longer have your physical hardware (on-premises infrastructure). This results in lower costs compared to a private cloud because, in a private infrastructure, all server resources are exclusively reserved for you, and you are billed accordingly.
When you work in the public cloud, sometimes referred to as the open cloud, a cloud provider takes care of the underlying infrastructure. Due to the use of virtualization technology, you are unlikely to notice much of this: the infrastructure is designed to accommodate a multitude of customers and is perfectly scalable. In the public cloud, each user can increase or decrease their allocated capacity at any time.
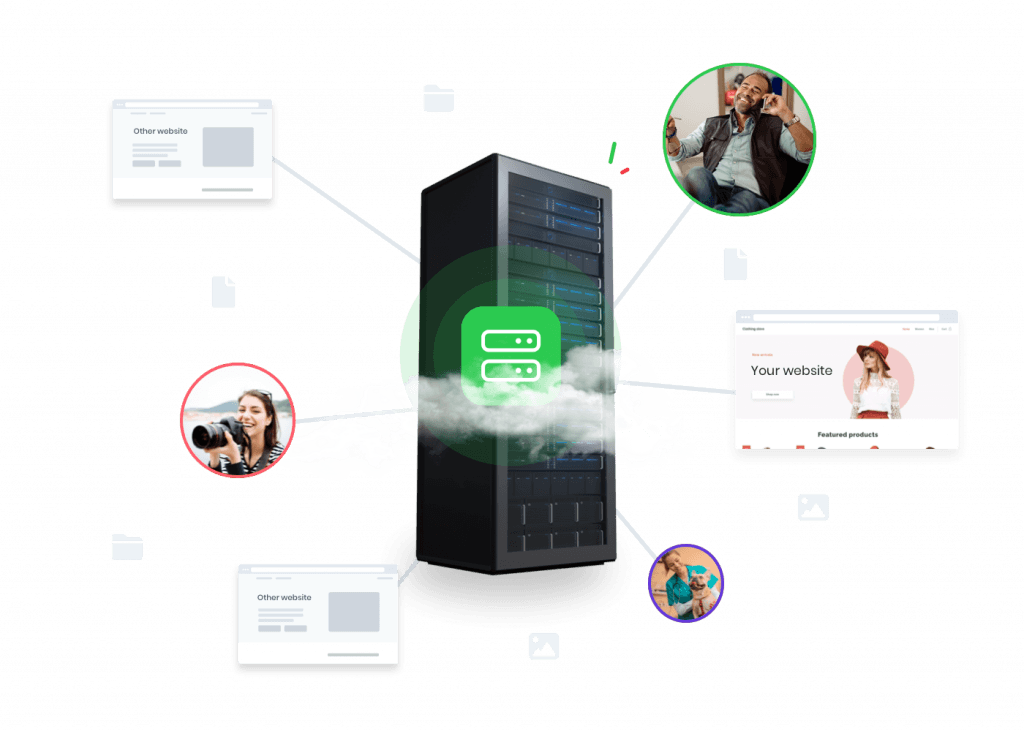
In both public, private, and hybrid clouds, you have the option to store your data with major international public cloud providers or local providers. Well-known providers include Amazon Web Services, Google Cloud Platform, and Microsoft Azure.
However, there are many benefits to working with a local player like Combell. Consider having your dedicated server with specific Service Level Agreements (SLAs) and performance guarantees, which we will delve into later in the blog.
Also read
Key elements of the public cloud:
What you need to know about private clouds
Now, let's shift to another type of cloud computing: the private cloud. As mentioned, with this cloud solution, you do not share resources; everything is essentially yours. It guarantees full control over your data. You can also access private cloud services from the same cloud providers.
Key elements of the private cloud:
Tip
Don't be discouraged by the costs of a private cloud. Especially for larger companies, transitioning to this type of cloud computing is often a better choice. Managing multiple clouds can end up being more expensive compared to a well-organized private cloud environment.
What you need to know about hybrid clouds
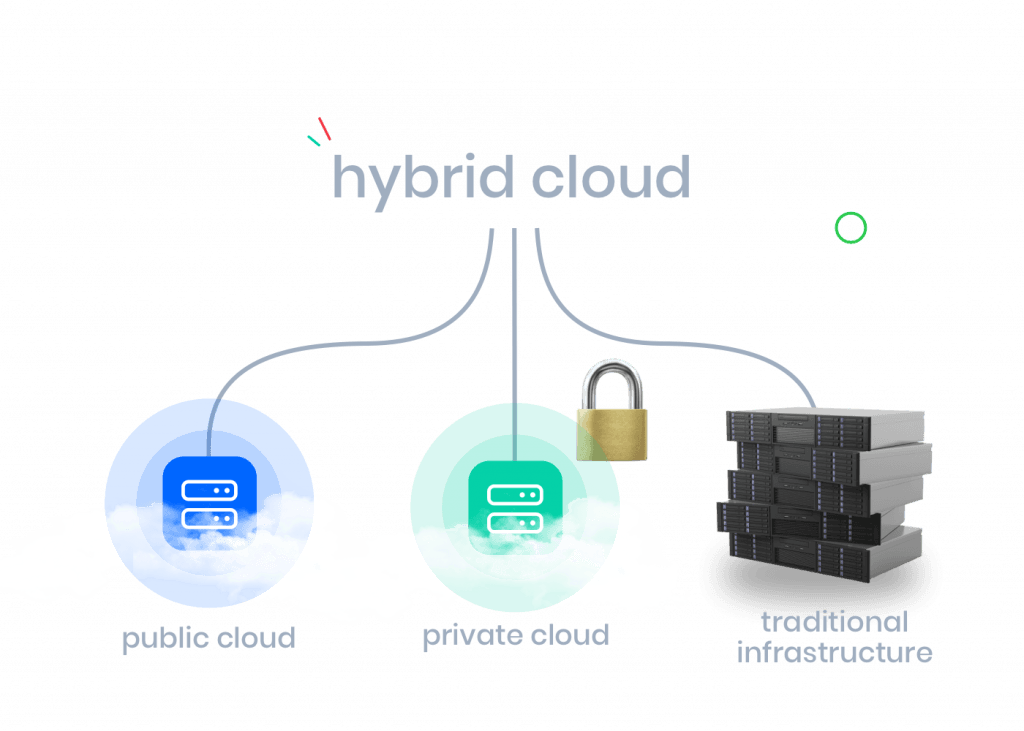
What about a hybrid cloud environment? A hybrid cloud is essentially the best of both worlds, although there are various definitions of what constitutes a hybrid cloud. Some sources consider it a hybrid cloud when it combines cloud services with on-premises solutions or dedicated servers from a cloud provider.
Our definition of a hybrid cloud is more specific:
A hybrid cloud is a combination of one or more private and public clouds. It's crucial to provide the right technical solutions to these environments so that end-users do not notice they are working in different environments.
This combination is highly appealing to many companies, either because they prefer to keep certain mission-critical applications and sensitive data within their own premises, while less critical applications can reside in the cloud.
Alternatively, it can be the opposite: critical applications in a private cloud with a managed provider (for maximum security and continuous monitoring) and less critical applications in-house or in a public cloud.
In such a hybrid solution, the public cloud offers flexibility and scalability to the part of the infrastructure that experiences specific peaks in demand, while the private cloud provides more certainty in terms of performance and data protection.
Important elements of the hybrid cloud:
Which cloud is suitable for your company?
Well, that's the hundred-million-dollar question! There is no one-size-fits-all answer because each company has different needs, requirements, and expectations. That's why it's essential to carefully assess certain advantages and disadvantages in advance and make the right choice based on that.
Also read
Furthermore, there are significant differences among providers themselves. Not every public or private cloud is the same: prices vary, the level of security can differ, and the offered services often vary as well. Even among public cloud providers, there are distinctions between international giants and local providers.
Importance of cloud services
That's why it's crucial not only to thoroughly weigh the pros and cons in advance but also to take a closer look at the various players and their offerings. In this regard, (additional) cloud services are of paramount importance. Here's what you should consider:
1. What are the terms and conditions?
With an international provider, you may need to adhere to the standard terms and conditions that the provider has established for all customers. However, not every public cloud provider offers the same terms and conditions, and not every customer has the same needs. For example, some cloud providers offer everyone a standard 30-day backup. For some customers, this may be insufficient, while others may feel they are paying for more than they need.
Also, pay attention to what is not included in the price. Often, there are hidden costs such as data transfer fees that can lead to unpleasant surprises. The Combell public cloud is different... While it doesn't involve shared hardware, you do have your dedicated server, isolated from other cloud servers. You have your own SLA, guarantees, and performance assurances.
2. Is there support provided?
With a local provider like Combell, you can enjoy excellent support in your own language. Our support team is genuinely accessible, and you won't be endlessly transferred from one representative to another. You'll be assisted by local experts. This is in contrast to cheaper providers.

3. How solid is the Service Level Agreement (SLA)?
Private, public, hybrid cloud... No matter what you choose, it's always important to negotiate good Service Level Agreements (SLAs). An SLA outlines the service your cloud provider promises in terms of availability, performance, and the support you can expect when something goes wrong.
Think carefully in advance about what you want and what's essential because the budget often increases exponentially as you demand stricter SLAs. It's not just uptime that's important, but also who manages what. Are you only renting computing power and relying on your IT team to manage your private cloud or virtual data center? Or do you want to avoid headaches and opt for a cloud that is entirely managed for you?
4. Do you get guarantees when something goes wrong?
Also, look into guarantees for problems. When things go wrong, you want a quick solution. It's essential to check the guarantee regarding the time frame within which your provider promises to have a resolution. Many cloud providers opt for a Mean Time To Recovery (MTTR), where you agree on an average recovery time.
However, this approach has its drawback: if your provider can fix something ten times within a few minutes and takes several hours the eleventh time, they still meet your MTTR agreements. Yet, you experience hours of downtime. This is why the presence of a helpdesk at a local public or private cloud provider is crucial.
5. What about the "Nines"?
A guaranteed uptime of 99.9% might sound like a lot, but it allows for about 8 hours of unplanned downtime per year. In contrast, with a 99.999% guarantee, you are allowed less than six minutes of unplanned downtime per year. Reducing downtime from hours to minutes ensures that you don't lose customers, communication, productivity, and revenue!
6. How reliable is the provider?
Have there been issues with the cloud provider, and how were they handled? What was the communication like during those incidents? Because, let's face it, it's essential to be properly informed when there's a problem so you know what's being done to resolve it.
Are there clear agreements regarding contract termination? Have you determined whether you have the right to retrieve your data and applications from the cloud at any time? And what are the associated costs?
7. What about the technological requirements of cloud computing?
Beforehand, consider not only the functionality you need but also technical requirements and performance. Not every application works the same way. Some applications require more memory or processing power, and some websites need to handle spikes in visitor numbers.
In an international public cloud, you deal with average server performance or choose between faster and slower storage capacity. If that's not sufficient, you should consider an isolated public cloud, private cloud, or hybrid cloud: they are built entirely to your technical specifications. This helps you avoid storage or performance issues.
Furthermore, there are data security and data privacy concerns. How is your data protected? Does it need to stay within your country or the EU? Who has access to your data? What about backup and the ability to quickly recover? Often, these aspects are related to technological choices, so ensure you understand what you're getting in these areas as well.
8. Do you have a sufficient budget?
A third element to consider in your decision is financial in nature. What about your budget? A private cloud has a higher initial cost but lower costs with higher usage. A public cloud has a lower initial price but becomes more expensive to scale. This is logical because there is much more variability in the offering.
This means that there is often a tipping point as you grow in the cloud. At a certain point, for purely financial reasons, it becomes more interesting to transition from a public to a private or hybrid cloud. Calculate this tipping point yourself and determine it in advance. A good cloud provider can certainly advise you on this.
9. How secure are your Data?
When weighing the pros and cons of a private versus public cloud, data security is often a crucial argument. Generally, a private cloud offers more assurance in terms of data security. This might seem obvious, but the difference in security between a public and private cloud is often not as significant as you might think.

As explained earlier, not all public clouds are created equal. Cloud solutions offered in the form of Software-as-a-Service, for example, may have less separation between user data than Infrastructure-as-a-Service clouds, such as the Combell cloud.
The latter group should have built-in separation between the various virtual cloud servers, provided by a good cloud provider. So, don't just scratch the surface when it comes to data security; be sure to ask detailed questions.
Misconception
Conversely, there is often a misconception that data stored on shared storage systems can be easily accessed by all users. This is also a misconception. In a public cloud, you can just as easily separate virtual storage as you can in a private cloud.
Each Storage Area Network (SAN) – the actual storage space - is controlled by software that stores user and security settings. This software does not distinguish between hardware used by 100 customers or just one.
Every European company must comply with GDPR, but certain professional sectors have even stricter rules for storing (sensitive) data. While nowadays all storage is controlled by software, and there is actually little difference between storage units on a shared or private network, it may still be mandatory to use your hardware to comply with certain (legal) regulations. At that point, a public or even a hybrid cloud is not an option.
Your needs and requirements as our starting point.
In conclusion, look for a provider that aligns well with your needs and demands. Examine the functionality you require or prefer and see who can offer that. Ideally, you'll find a provider who allows you to create a sort of menu with the things you want and don't want. 😃
If you can't find anyone who offers what you're looking for or if the imposed regulations don't fit your company, it's probably better to opt for a local public, private, and/or hybrid cloud. To assist you, we can match you with the right cloud solution.