For Internet users, it is very simple: if you want to visit a web page, you just have to enter the name of the website into a browser, and you will instantly arrive at the right place. But whoever takes a first look at what is going on behind the scenes of the Internet will most likely be overwhelmed by technical jargon, with terms like DNS, name servers or domain names. If only there was a simple explanation… But wait, there is one! And you can read it below!
What is a domain name?
A domain name is the address of your website. It helps your visitors understand what they need to type in the address bar of their browser to get to your site.
Every website needs a domain name. If you take a moment to check this in the address bar of your browser, you will see that the domain name for our website is combell.com. You can see that the domain name consists of two parts: a name – Combell – and a domain extension: .com.
Anyone can register a domain name. However, be careful: when you register a domain name (or domain), it does not mean that you immediately have a website online. For that, you also have to create a website, which you then have to upload to your web hosting. You can read more about this below.
Why is a domain name important for your business?
Registering a domain name for your company has many advantages, even if you decide not to link a website to it right away.
- When you register a domain name, no one else can walk away with it. Because as long as you do not register your domain name yourself, anyone can buy it on a first come, first served basis. And of course, it would be a shame if your competitors were to beat you to it, eh?
- Having your own domain name comes across as very professional. With Combell, you get free e-mail addresses with your domain name, which is really convenient for your business cards. The days you had to use clumsy e-mail addresses like mycompany@hotmail.com are definitely over! You have to admit that info@mycompany.be looks so much neater!
- Your online presence is very important. It helps potential customers to find you without any difficulty.
How does a domain name work?
If you want to know how a domain name works, we should first take a look at how the Internet works.
The Internet is a gigantic collection of computers, which are all connected to each other by cables: a worldwide network – also known as the World Wide Web. All computers in the network can communicate with each other. And each computer hosts a website.
Of course, that adds up to a lot of computers, and it is therefore necessary to create order out of that chaos. That is why IP addresses exist. These are unique names for each computer, thanks to which other computers immediately know how to reach each other.
Just as a person can be named Peter Johnson, a computer can be named 217.21.190.142. Each IP address exists only once: this way, each computer has a unique name, and no confusion is possible.
Since computers have a slightly larger memory than humans, it is no problem for them to remember all those IP addresses. But imagine if you had to type in 217.21.190.142 every time you wanted to visit Combell’s site. Or 142.251.33.99 to use Google. That would not be very convenient. That is why we have domain names: they point to IP addresses and are much easier to remember.
As an Internet user, you set an entire network in motion when you visit an address – or domain (name).
- You enter a domain name in the address bar of your browser – for example: combell.com.
- A request is sent from your computer to a worldwide network of computers (servers): the Domain Name System (DNS): “I want to visit combell.com”. The DNS is the system that, with the help of a lot of information (DNS records), ensures that an Internet user who has entered a domain name in his or her browser arrives at the right place. Click here to find out (a lot) more about the DNS.
- The DNS looks at the DNS records to know via which name servers it can guide you to combell.com, and forwards your request to them. Name servers are computers that are managed by your web hosting provider.
- These name servers then forward your request to the computer where combell.com is hosted: the web server.
- The web server collects all the components of combell.com that you need, and sends all the data (i.e. the web page) back to your browser.
What types of domain extensions are there?
A quick reminder: a domain name looks like this:

The choices for the name of your website are endless: as long as nobody else has registered it yet, you can buy it.
Domain extensions, on the other hand, are limited: there are only a few domain extensions – ‘top-level domains’ or TLDs – to choose from. These TLDs are managed by ICANN, and new ones are regularly brought to the market. They can be divided into a number of categories.
1. Country Code Top Level Domain – ccTLD
Each country has its own country code. For Belgium, it is .be, and for the Netherlands, .nl. It always consists of two letters. In most cases, you do not have to live in a certain country to be allowed to register a domain name with that country’s country code. Using the ccTLD of another country is often a good way to attract visitors from that country.
EXAMPLE:
Frank has a company that makes furniture and wants to focus on the French market. He can thus perfectly register the domain name furniturefrank.fr from Belgium or the Netherlands. This will allow Frank to be found more easily on the Internet by Internet users searching for furniture in France.
2. Generic TLD – gTLD
A generic top-level domain does not belong to a specific country (like a ccTLD). Examples of gTLDs are .com, .org, .amsterdam or .gent. The latter two are examples of new generic top-level domains (new gTLDs).
3. Sponsored TLD – sTLD
sTLDs represent a particular sector. For example, the sTLD .travel exists for the travel industry, .post exists for postal services, and .xxx exists for… well… you know!
What is the difference between a domain name, a website and web hosting?
A domain name without a website linked to it is like an address without a house: it is not very useful. If you want a website, you need both a domain name and web hosting to host it on.
Simply put: If you think of your website as a house, then your domain name is your address, and your web hosting is the plot on which you have built your house.
Example:
Steven is a baker who wants to have his own website to promote his bakery. Steven needs a few things for this:
- A domain name: this is the address of your website. For this, you should choose a meaningful name, like bakersteven.be.
- A website: that is the collection of all the pages you can find via your domain name.
- Web hosting: that is the space you purchase on which you can upload the photos and all other content of your website. Just as you need disk space to store photos on your own computer, the same is true on the Internet. The only difference is that this space is located somewhere else: on the computer (the ‘server’) of your web hosting provider.
- Possibly a website builder. This tool allows you to build your website very easily.
The domain name does not necessarily have to be purchased from the same provider as your web hosting. If you bought them from two different companies, you just need to change the settings of your domain name in the control panel of the company where you registered the domain name. There, you must enter the information about the name server that you received from your web hosting provider so that the DNS (as described above) knows which server to send your visitors to when they enter your domain name in their browser.
How can I purchase a domain name, and how much does it cost?
There are many companies that offer domain names. Such providers are called ‘registrars’. They are the ones that contact the appropriate organisation on your behalf in order to register your domain name.
All you have to do to register a domain name is to check whether the domain is still available. If your domain name is still available, you can immediately register it. When you register a domain name with Combell, you also get free e-mail addresses and a mailbox to store your e-mails.
A domain name is not necessarily expensive. Combell works in a very transparent manner, and we always run special offers.
Be careful though, because as mentioned above, a domain name is not the same as a website. For that, you also need hosting. When you purchase web hosting from Combell, you can also register your domain name for free. That way, you will be up and running in no time!
FAQ about domain names
What is the difference between a domain name and a URL?
A domain name is the name of your website, like combell.com, for example. A URL (Universal Resource Locator) is the address of a specific page on your website. Each URL contains a domain name, together with other elements that are necessary to reach a certain page.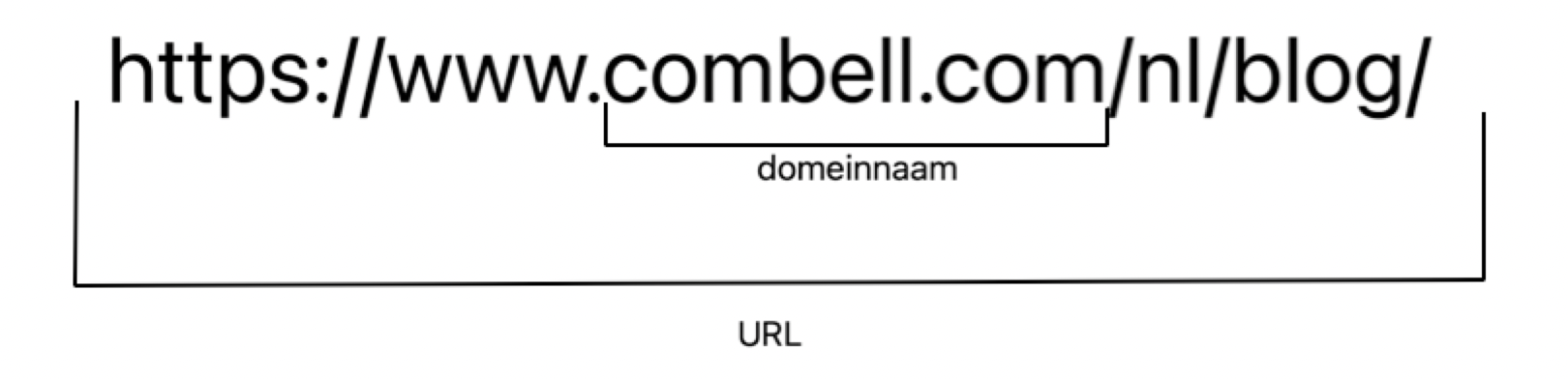
What is a subdomain?
A subdomain is an extension of your domain name, which helps you maintain a clear structure for your website. You can create as many subdomains as you like (up to 500 per domain name).
The address of a subdomain looks like this: subdomain.yourdomain.com. For a web store, you could e.g. use shop.yourdomain.com.
Click here to learn everything there is to know about subdomains.
What is the difference between a registry, a registrar and a registrant?
A registry is an organisation that is responsible for a certain domain extension. You cannot purchase your domain name directly from a registry; for this, you need to turn to a registrar.
A registrar is a company that sells domain names. However, not just anyone can sell domain names: a registrar has to meet strict requirements. In order to purchase a domain name, the registrar contacts the registry on behalf of the registrant.
A registrant is someone who registers a domain name with a registrar. In other words, anyone who has registered a domain name is a registrant.
Example:
You would like to register yourdomain.be. You then check with a registrar, such as Combell, whether this domain name is still available. Once this is done, the registrar contacts the registry (for the domain extension .be, this is DNS Belgium) to register your domain name on your behalf. Once yourdomain.be has been registered, you are the official registrant of this domain name.
What is DNS (Domain Name System)?
The Domain Name System (DNS) is the system that ensures that a visitor who types in a domain name arrives at the right place. The DNS uses all kinds of information for this: DNS-records.
Can I sell domain names?
You can sell your own domain name, just like you would sell a bicycle on eBay. There are certain ‘online marketplaces’ for this purpose: trading platforms, such as sedo.com (short for ‘selldomains.com’, just in case you did not get it). There, you can auction your domain name (among other things).
If you have ever purchased a popular domain name – for example, ‘website.com’ – that domain name could bring you a lot of money!
Can I link my website to another domain name?
You can easily link your website to another domain name, as long as that domain name is in your possession. By editing the DNS records (more specifically, the A records of the name servers) of your domain name in the control panel of your domain, visitors will be able to reach your website via that domain name.
Here you can find out what DNS records are and how you can edit them

